
The global outlooks of the legal market of cannabis are excellent. It is possible to simultaneously imagine dry law repeal and craft brewing boom but not in one but in several consumer categories. For alcohol is contained in liquids and cannabis derivatives can be in three physical forms.
The value of legal market of cannabis and its products can reach 10% of the world beer market in five years, and in 2030-2040 even reach the same scope provided the current rates of legalization and development of market infrastructure remain at the same level. Cannabinoids are actively integrating into the food industry from chewing gum to beverages deforming the pharmaceutical and alcohol markets, they influence the trends of healthy lifestyle and beauty.
Cannabis is constantly discussed in business media and surveys of investment analysts. Only in the beverages industry such giants as The Coca-Cola Company, AB InBev, Heineken, Molson Coors and Constellation Brands have already gone in business and shares and some other transnationals are engaged in talks with cannabis producers. Thus, despite the beer subject-matter of the journal, we cannot ignore the trend that is already impacting the world beer market…
From synapses to legalization
New consensus?
Endocannabinoid system: more than a switch
Cannabinoids’ path to brain
THC: 50 of green shades
CBD: almost a panacea
CBD vs THC: balance and control
Cannabis status
Legalization, decriminalization or tolerance?
What WHO recommends to UN
Global market of cannabis
Consumer’s profile
Patchwork quilt
Legal market of cannabis
Californian case
Segment of medical cannabis
THC Pharmaceuticals
CBD: Rocket market
Regional status
CBD market
THC vc alcohol
Two groups
Score11:1
Two-storey market
Cannabis and beer
We can objectively observe gradual lifting of prohibition and a fast growth of capitalization and sales of cannabis producing companies. This is shown by the North America that is rapidly approaching complete legalization of recreational consumption of cannabis and about fifty countries more where medical usage of cannabinoids is regulated.
Where possible, cannabis and its derivatives with psycho-active tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are imperceptibly taking over the old good alcohol as it is considered to be a less harmful alternative.
The second rising star is non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD). It not only mitigates dangerous effects of THC and other stimulators (including alcohol) but also as an independent product is in tune with modern trends of healthy lifestyle, modern medicine, biohacking and responsible consumption. At the same time, it has originality and intriguing link to cannabis. In 2018 CBD gummies took the third line of category Food of the search rating of Google Trends USA.
At the end of 2018, there appeared serious preconditions for wide usage of cannabis for medical purposes. WHO experts recommended to exclude cannabis from the list of dangerous narcotic substances on carrying out official critical research. This amendment is final and will be sooner or later approved by United Nations commission despite the politization of this process.
Even in conservative societies if there is evolutionary logics, the attitude to cannabis can change due according to the effects given by it.
The first stage of cannabis acceptance is connected to affirming effectiveness of medicines on the basis of THC and CBD in treating a wide range of diseases. Their image in the world expert community was substantially improved due to discovery of endocannabinoid system and a surge of articles in the key medical journal.
«Metaphorically the endocannabinoid system represents a microcosm of psychoneuroimmunology or mind-body medicine» said John M. McPartland, famous American neurobiologist. Obviously, cannabinoids of plant origin are the key to this microcosm. In this context, the global legalization of non-psychoactive CBD looks an issue of the nearest future. At the same time, THC lack of options in controlling chronic pain, depression, anxiety and psychic disorders builds a link from medical to recreational consumption, which disturbs the public consensus.
As we can see, the estimation of cannabis market outlooks demands understanding of its functional features that can be complicated and opposite. To do this we need to describe the human endocannabinoid system and effects of two main cannabinoids THC and CBD.
In this article we have attempted to generalize the most interesting practical information from Pubmed (database of medical and biological publications) and not make the text too complicated with biochemistry. Special attention has been paid to consumer profile analysis and models of interaction between alcohol and cannabis markets.
We have looked at state regulation of production, consumption of cannabis products in different regions. We analyzed the volume and potential of legal cannabis markets and their segmentation.
From synapses to legalization
New consensus?
Cannabis is a product with multivalued reputation in the society:
- Many adults have a stigmatized attitude to cannabis consumption as they link it to drug-addiction, anti-social behavior of teenagers and marginal subcultures.
- Broad-minded millennials often support the legalize movement.
- People with chronic and severe diseases see a possibility to alleviate their suffering.
- Politicians, opinion leaders, journalists and other hype-lovers find an excellent chance to attract attention.
- Pharmaceutical and FMCG companies foresee a huge potential of the legal cannabis market so they turn to their lobbying power in order to open or on the contrary overregulate this market feeling either perspectives or danger.
- Besides, there is a wide range of doctors’ opinions in various medical professions, as well as interests of drug business and law enforcement authorities, etc.
Thus, one can see a lot of interest conflicts and different opinions that require a critical approach in case of the status quo changes. On the one hand, it should not be a light-hearted approach to cannabis as to absolutely harmless product (which is not). On the other hand, one should avoid improper moralization as cannabis and its derivatives are often used not only for fun.
Consensus as to gradual legalization of cannabis consumption is only possible under the condition of understanding how it influences human body and behavior. For a long time that was uncertain, and only 30 years ago scientists learnt that our body produces cannabinoids of its own. At that moment the list of known neurotransmitters was enriched with very unexpected substances that save the brain from overwork.
The key difference of cannabis and its derivatives from alcohol, opioids, cocaine and other psycho-stimulants is a potential to improve the psychological, emotional and physical condition. And the cannabinoids do not take a transitory position between alcohol and heavy drugs as they are too different from them by their properties, additive effect and toxicity.
The balance of active substances has the key significance. For instance, comparing to stimulants is inadequate if we speak of cannabis or drugs containing high doses of cannabidiol (CBD that compensates the effect of psychoactive substances.
Cannabinoid researches have already given surprising results setting trends in medicine and the number of publications on this issue is growing exponentially.
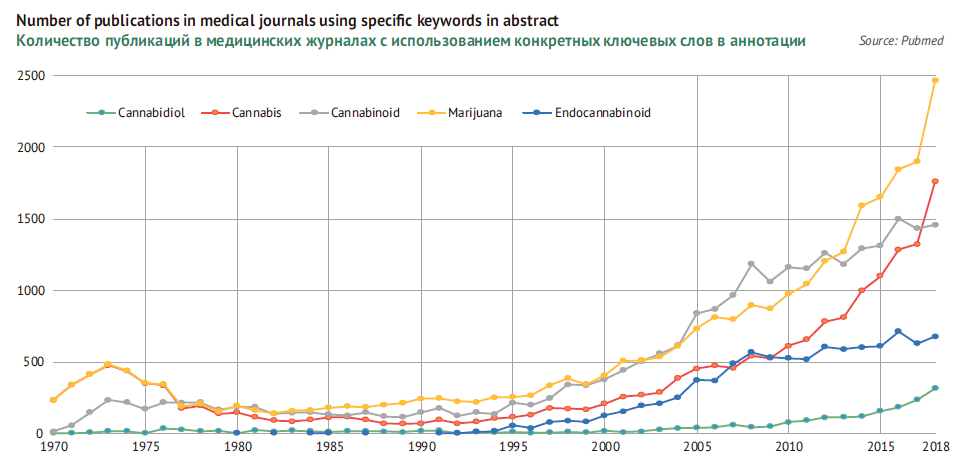
Cannabinoids can be useful for solving major health problems of the modern humanity that are connected to ageing, stress, deterioration of ecological conditions, etc. Cannabinoids are effective in treating many severe and chronic diseases that are resistant to treatment or where side effects offset benefits. Doctors are getting rapidly aware of promising effects of cannabinoids and more often use it.
At the same time, nobody can deny the danger of frequent and heavy use of cannabis for pleasure. Cannabinoid THC due to its multiple effects, influences the same centers of reward as alcohol, cocaine, opioids, so it can lead to additive effect (addiction and dose increase). Choosing products with high concentration of psychoactive substances can result in situations we will tell about in the chapter on THC properties.
As we can see, medical and the more so recreational legalization of cannabis is possible in case of effective state regulation based on understanding the complex properties of cannabis.
Endocannabinoid system: more than a switch
“Relax, eat, sleep, forget, and protect – the basic effects of endocannabinoid system” – Dr Vincenzo Di Marzo
In the international scientific classification cannabis is divided into the main species Cannabis sativa (common hemp) and its wide-spread subspecies Cannabis indica (Indian hemp).
In the essence, it is important to remember that indica has a pronounced psychoactive effect, as it contains more tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The main species sativa (or, more precisely its industrial sorts) is currently used for textile fibers, hemp oil and sometimes cannabidiol (CBD).
To better understand the effects of cannabinoids THC and CBD on humans, we will further generalize the practical and most interesting info on endocannabinoid system.
Basing on analogies with psychoactive effects of coffee, alcohol and drugs scientists expected 1) cannabis to have some active substances 2) organism to have ways to transport them, 3) nervous system to have entering points they influence. It was obvious for researchers who had been trying to find the psychoactive component of cannabis for 150 years. But as it became criminalized in 1920-1971 such researches got not very actual and complicated by prohibition on even medical use.
In the middle of the previous century, major scientific centers dealt with a scale and actual for medicine issues (for example opioids researches). And small laboratories far from leading scientific centers that could not expect a big financial support, focused on less ambitious tasks. So, the issue of cannabinoids was for the first time seriously taken by a small Israeli laboratory in the middle of the 60-ies. This for a certain time determined Israel’s scientific leadership in developing medicines based on cannabis.
 Thus, early in the 1960-ies, biochemist Raphael Mechoulam from Weizmann institute (Jerusalem) started researching chemical structure of cannabis. He managed to divide the cannabis extract into many components – cannabinoids. It turned out that only one of them has psychoactive properties, comparatively the same as appear when using cannabis. Raphael Mechoulam managed to obtain enough pure substance in 1964 and published the chemical formula of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Thus, early in the 1960-ies, biochemist Raphael Mechoulam from Weizmann institute (Jerusalem) started researching chemical structure of cannabis. He managed to divide the cannabis extract into many components – cannabinoids. It turned out that only one of them has psychoactive properties, comparatively the same as appear when using cannabis. Raphael Mechoulam managed to obtain enough pure substance in 1964 and published the chemical formula of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
THC was liposoluble and in that way differed from most of psychoactive drugs and human neurotransmitters that are on the contrary can be dissolved in water.
The discovery got a wide publicity but only among scientists. Though several drugs were patented for medical use, at the beginning, pharmaceutical companies did not see a big practical significance in it.
 At the end of the 80-ies Raphael Mechoulam who had received the degree of professor and a chair in Jewish university, continued researching cannabis. He proposed a logical hypothesis on existing of specific cannabinoid receptors interacting with THC. In 1988, these receptors were found in cooperation with American researchers, who studied THC routes in animals’ bodies by giving THC a radioactive mark.
At the end of the 80-ies Raphael Mechoulam who had received the degree of professor and a chair in Jewish university, continued researching cannabis. He proposed a logical hypothesis on existing of specific cannabinoid receptors interacting with THC. In 1988, these receptors were found in cooperation with American researchers, who studied THC routes in animals’ bodies by giving THC a radioactive mark.
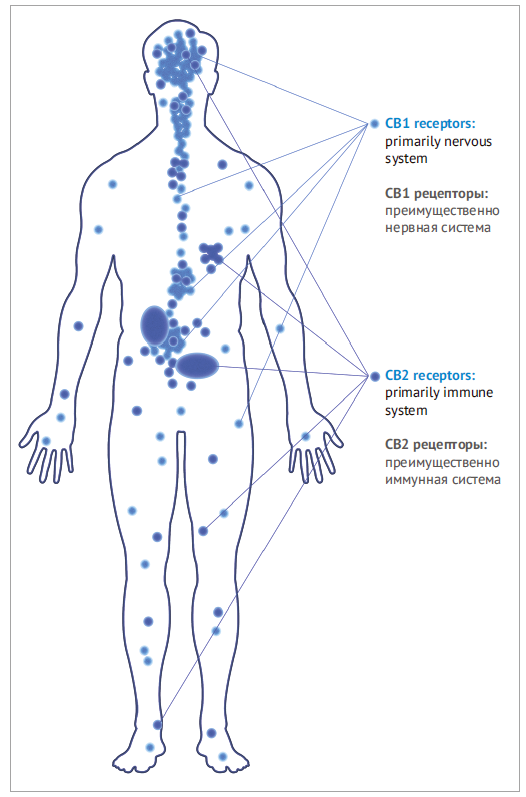
The discovered receptors were called CB (CB1 later). They had an unusual structure, formed one of the most numerous groups and turned out to be present in various parts of brain and spinal cord. Later on cannabinoid receptors were found in the peripheral nervous system (heart, lungs and gastrointestinal tract) and cells connected to immunity.
These discoveries explained the multiple effect of cannabis consumption – effecting emotions, memory, appetite, motor activity change and others. They also cleared the various reactions to cannabis due to differences in the nervous system organization and metabolism. Thus, about 20% of people refuse cannabis forever due to unpleasant sensations.
Further studying of cannabinoids raised new questions. Hungarian scientists found out that cannabis works as a “switch” of agitation. It became obvious that there is an endogenic cannabinoid which is produced by the body. But for a long time, it was not known, what kind of substance it is and what its role is.
The first endocannabinoid was discovered by Raphael Mechoulam 28 years after he published the formula of THC. There was not a proper name for the substance in Hebrew or Farsi, yet there was one in Sanskrit, anandamide (Ananda means joy, happiness). This was a good name taking into the account the long history of cannabis consumption in India. Soon after the American researchers discovered the second not less important endocannabinoid, 2-AG.
Like THC, anandamide was found to have liposoluble structures, yet for some reason they are inside nervous cells and not outside as other neurotransmitters.
The key role of endocannabinoids was defined by American and French researches early in the 90-ies. It was found out that the liposoluble structure, the original location inside nervous cells and most importantly, the route of endocannabinoids in the direction opposite to the main “traffic” in neurons enabled the nervous system to develop a function of feedback. In professional literature it acquired name “retrograde signalization”.
Each neuron communicates with other neurons by means of synaptic clefts between terminals. Outgoing long terminal (axon) that passes information connects to incoming terminal (dendrite) receiving information. The signal transmission from axon to dendrite takes place by erupting of a neurotransmitters from a special bag (vesicle) on the axon surface. The neurotransmitters get in the contact place (synaptic cleft) where they function as an electrical switch. This is the way the normal presynaptic-postsynaptic traffic of signals works.
However, cannabinoids unlike other neurotransmitters are not stored anywhere. They are rapidly produced by nervous cells and can get inside the membrane due to its liposoluble structure. And unlike other neurotransmitters, they travel backward – from dendrite to axon. On axon they activate cannabinoid receptors CB1, which leads to temporal decrease of usual neurotransmitters production.
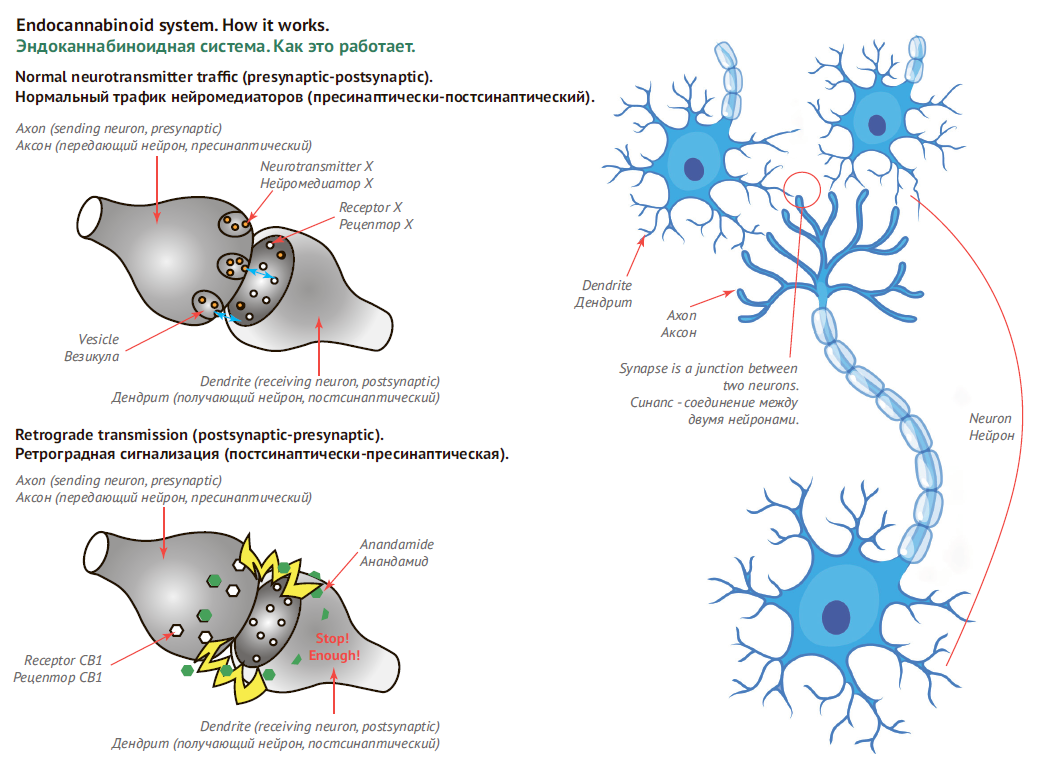
Figuratively, the system operation can be described so: at surplus stimulation that can lead to injury or death, nervous cell rapidly produces and releases endocannabinoids, thus giving the signal – “It is too much for me, stop the stimulation!” And due to the liposoluble structure of the molecules, they do not expand to the cerebral fluids to distant parts of the brain but rapidly leave via the transport system.
Thus, in the brain endocannabinoids often play a defensing function of “fire brigade” suppressing dangerous agitation at local sites of brain.
Beside CB1 there were found special receptors of the second type (CB2) located in spleen and peripheral tissues that are connected to immune system and often activate in case of diseases. There are probably other cannabinoid receptors, recently there have been articles on possibilities of cannabinoid impact on non-specific for them receptors.
 Cannabinoids role is much more than just “switchers” of agitation in nervous cells. Here are some of known effects of endocannabinoid system activation.
Cannabinoids role is much more than just “switchers” of agitation in nervous cells. Here are some of known effects of endocannabinoid system activation.
It helps the brain to forget worries, relax and get rid of unproductive and anxious behavior models. For example, in the course of experiment, animals deprived of endocannabinoid receptors continued be scared of the signal connected to hurtful experience even if it had not been repeated for a long time.
Another function is linked to the fact that the array of agitation and inhibition in the nervous cells that are modulated by cannabinoids turns out to be necessary for learning new information.
Cannabinoids play an important role in the immune system regulation and its respond to infections. Endocannabinoids 2-AG and CB2 receptors are essential here.
But in fact, the endocannabinoid system has either direct or indirect influence on all physiological systems and organs in the body from emotions to bone regeneration.
Cannabinoids’ path to brain
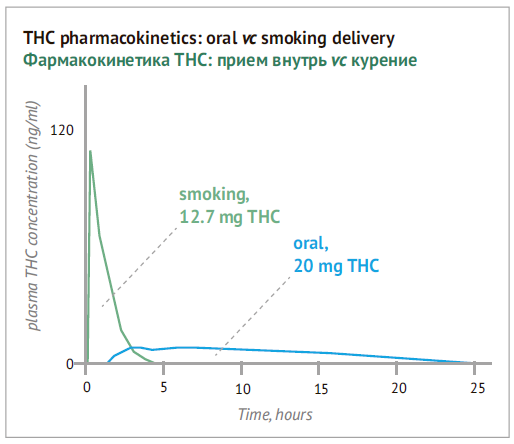 Cannabinoids are commonly inhaled or swallowed. Depending on the intake way, the speed of THC and CBD effect varies much. For psychoactive cannabinoids, there is a problem of their action acceleration in order for the person to understand whether it is time to stop.
Cannabinoids are commonly inhaled or swallowed. Depending on the intake way, the speed of THC and CBD effect varies much. For psychoactive cannabinoids, there is a problem of their action acceleration in order for the person to understand whether it is time to stop.
In particular, taking cannabis in foods though seems the simplest and most attractive, is not very popular. When taken perorally, cannabinoids cannot just dissolve in blood plasma due to its structure, but involve the same transport routs as fats. Psychoactive effects of THC appear with a delay of 30-90 min. approaching maximum in 2-3 hours and last for 4-12 hours depending on the dose. The effect of such cannabis intake arrives much later and lasts much longer than, for example from alcohol.
In case cannabinoids are inhaled, effect comes faster than after alcohol consumption. After the first inhale when smoking (or during inhalation use via vaporizers), coming in through the lungs, THC gains the maximum concentration in the blood plasma within 3-10 minutes. The psychoactive effect starts in several seconds or minutes achieving maximum in 2-3 hours. Thus, though cannabis inhaling seems to be the least pleasant and most difficult way of consumption for recreational purposes, it is spread wider than peroral intake.
 The second aspect is low bioavailability of cannabinoids and big variations of concentration in blood depending on many factors. Though THC and CBD pharmacokinetics has been long the matter of many studies, producers of food supplements, pharmacologists and doctors find it difficult to achieve stable effects.
The second aspect is low bioavailability of cannabinoids and big variations of concentration in blood depending on many factors. Though THC and CBD pharmacokinetics has been long the matter of many studies, producers of food supplements, pharmacologists and doctors find it difficult to achieve stable effects.
Summarizing the data from various sources we can say that 6-12% of cannabinoids get into the blood by usual peroral taking, 2-57% is taken by smoking or inhalation. At that, it is very important whether cannabinoids are taken on an empty stomach or with other food, what kind of foods it is, what volume of vapor or smoke got into the lungs and so on.
Today vaporizers, sublingual oil forms, nasal sprays, chewing gums, transdermal way (creams) that promote quick entering into blood through mucous membranes or skin are considered to be promising for measurable and highly effective use of cannabinoids. Other ways to increase bioavailability that is, developing combined substances, for example, use of terpens (contained in cannabis), piperine (pepper extract) or dietary middle-chain fats. The most effective are special molecular forms of cannabinoids, that is, combinations with liposomes, nanoemulsions and others we will discuss later.
Having entered the blood, cannabinoids are metabolized by liver, accumulate in the tissues rich in lipids, i.e. brain, liver, lungs as well as cell membranes. Later the opposite process of discharging into the blood circulation takes place. In heavy cannabis consumers medical and police tests reveal traits of cannabinoids 13 days after taking.
Due to getting to the blood, plant cannabinoids act not locally but at many parts of endocannabinoid system. At the same time, there appears a lot of effects that can be undesirable in case of taking psychoactive cannabinoids.
THC: 50 of green shades
Pleasure from taking cannabis results from tetrahydrocannabinol effecting CB1 receptors in reward centers and serotonin receptors. Yet beyond pleasure there is a lot of effects that can be positive or negative.
How does THC influence the human body? Let us enumerate the most obvious and best studied effects:
1) The endocannabinoid system function of conquering non-productive fears and negative memories has opened prospects for cannabinoid use in posttraumatic and stress disorders. Here what matters is the influence on a deep and very important brain structure limbic system, that is responsible for managing fear, aggression, long-term memory and so on.
In particular, the braking action of THC on the amygdaloid body leads to various emotional reactions (normally positive) and emotional following of the long-term memory. In therapies such influence helps to return to usual life victims of aggression, war veterans, and other people surviving serious stress. Yet if the THC dose is too high or in sensitive patients on the contrary there can be anxiety or panic attacks.
 2) TCH effect on hippocamp and cannabis interference into the education function has various results. Some cannabis lovers are good at memorizing details and even raise their IQ. But the majority of people regularly taking it become on the contrary absent-minded because of “erasing effect” on different memory kinds. So that is why. THC is dangerous for growing organisms. By the way, one of witty theories explaining why the plants produce cannabinoids says that insects and animals eating leaves get disoriented and in a time are unable to remember where exactly they found them.
2) TCH effect on hippocamp and cannabis interference into the education function has various results. Some cannabis lovers are good at memorizing details and even raise their IQ. But the majority of people regularly taking it become on the contrary absent-minded because of “erasing effect” on different memory kinds. So that is why. THC is dangerous for growing organisms. By the way, one of witty theories explaining why the plants produce cannabinoids says that insects and animals eating leaves get disoriented and in a time are unable to remember where exactly they found them.
3) Motor neurons braking resulting from THC intake leads to physical relaxation and release of muscle spasm.
4) THC effect on hypothalamus leads to appetite growth. It also inhibits vomiting reflex which can be useful in case of motion sickness or necessity to take high-potent or toxic drugs that cause nausea.
5) Braking of excessive agitation in deep stem structures and spine marrow by THC makes the pain threshold much higher. So it is ever more often used as an analgesic in treating various painful conditions. This effect is especially useful in controlling chronic pain as it allows partially substitute much more dangerous opioids or ibuprofen with unpleasant side effects.
6) Braking of excessive agitation in the brain cortex allows controlling strong psychic reactions and epileptic seizures.
7) Influence on the second type (immune) receptors allows using THC in treating traumas and inflammatory diseases. Even cannabis effect was known in virtually all directions of ancient medicine and now it is being discovered again. However, frequent cannabis smoking can lead to various inflammatory diseases of the mouth, lungs, and other organs.
8) The mechanisms of THC effect on cardio-vascular system are very difficult as they include stimulation of peripheral nervous system (vagus nerve), brain centers and still unknown receptors in the heart and blood vessels. Due to such complex influence they speak of three-phase reaction to THC intake. The first phase of the reaction to the vagus nerve stimulation is sharp decrease of the heart muscle contraction rate and arterial pressure decline which lasts for only several seconds. Then the pulse rate rises and the arterial pressure goes a little up too which is then followed by a long-time decline.
Frequent THC consumption can easily lead to addiction as to drugs, alcohol, coffee, tobacco, some foods and so on. In this case in active cannabis consumers its withdrawal leads to abstinence symptoms – GIT disorders, appetite loss, irritation, anxiety sleep disorders. The addiction effect is connected to reduction of cannabinoid receptors and their constant activation.
According to WHO data, regular cannabis users can develop dependence on the drug. The risk may be around 1 in 10 among those who ever used cannabis, 1 in 6 among adolescent users, and 1 in 3 among daily users. If we compare the statistics of WHO by the age of cannabis users and other psychostimulants, cannabis is characterized by higher involvement of young consumers and their obvious decline with age.
On the one hand, the level of addiction and health risks by constant cannabis consumption in most of studies starting from 1993 (Gable) is considered to be much lower than in case of heavy drugs, alcohol and tobacco consumption. On the other hand, marginalization and criminalization of cannabis lower the threshold of negative perception of drugs. So adolescent consumers can more easily switch to heavier psychostimulants.
Besides, in adolescent and sensitive consumers by constant cannabis consumption such dose-dependent psychic disorders as psychosis, schizophrenia, anxiety, depression and asocial behavior can be observed. They however, last no longer than a month after withdrawal. In addition, THC action is considered to affect the brain and cause delays in development in children and adolescent.
There are specific problems linked to long-term and non-linear action of cannabis on motor and cognitive function of the body. There appear risks for driving, machine controlling, social communicating and others.
CBD: almost a panacea
While THC initiated the first interest to plant cannabinoids, currently consumers, doctors and researchers are more intrigued by non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD).
The content of CBD in most of hemp sorts is higher than THC, sometimes it can be virtually the only cannabinoid in considerable concentration. CBD is usually made of industrial cannabis with THC content regulated at (0.1-0.3%) maximum.
CBD lowers anxiety, the level of stress, helps in insomnia, yet due to absence of psychoactive properties its effects are not observed so soon and obvious. Though CBD does not connect to cannabinoid receptors or change the consciousness and motor functions, it has a pronounced modulation action on endocannabinoid system and otherwise.
How and why it happens?
Inside the nervous cells there is always cannabinoid formation and outside, there is always capturing and destruction of cannabinoids, which is particularly done by FAAH enzyme in the body. As CBD is structurally similar to endocannabinoids it is utilized the same way. Due to FAAH enzyme inhibition and competition for transport ways, CBD allows to slow down destruction of endocannabinoids.
 For example in a stress situation, nervous cells have to work out endocannabinoids and in a time they get exhausted. In case of CBD use, the destruction of endocannabinoids released by cell is slowed down sharply which compensates for their deficit. This in the first place happens where it is necessary.
For example in a stress situation, nervous cells have to work out endocannabinoids and in a time they get exhausted. In case of CBD use, the destruction of endocannabinoids released by cell is slowed down sharply which compensates for their deficit. This in the first place happens where it is necessary.
Due to its neuroprotective properties CBD helps for epilepsy, the condition of nervous exhaustion, chronic pain and psychic agitation. Today there are researches on treatment of inherited and age neurodegenerative diseases that have become a serious problem as the life expectance of people grows.
The list of CBD effects does not end at nervous system, it is very wide. Recently there have been a lot of articles on positive experience of CBD application in treatment of glaucoma, inflammatory diseases of GIT, diabetes, injuries of bone tissue as well as autoimmune disorders such as asthma, disseminated sclerosis, arthritis, schizophrenia, cancer, encephalomyelitis and others.
It is still not completely clear how exactly CBD helps to fight inflammation, as CBD does not activate immune receptors CB2 (they are activated by THC). However, the researches prove that CBD stimulates migration of protective cells and lower release of inflammatory cytokines.
The relaxation effect of CBD on the cardio-vascular system is according to researchers connected to existence of still unknown receptors regulating the work of vessel cells.
CBD vs THC: balance and control
Interaction between CBD and THC raises big practical interest as their proportion define the effect. And the main thing here is not only the fact that the both cannabinoids are contained in the same plant and interact with each other. It is also in the cannabis community that consumer of CBD and THC-based products creates to communicate in the countries with tolerant attitude. For example, according to Brightfield Group in the USA 70% of CBD consumers also consume other products where THC dominates.
It is known that CBD mitigates pronounced psychoactive properties of THC and prevents some undesired effects such as rapid heartbeat, anxiety, hunger and so on. Doctors recommend not to use CBD-low cannabis (or products with high THC concentration) due to higher risk of psychic disorders.
 Currently we have two scientifically confirmed explanations for CBD and THC interaction.
Currently we have two scientifically confirmed explanations for CBD and THC interaction.
The first one is that CBD can link to a part of cannabinoid receptor CB1 but does not turn it on but changes the form. After that THC is no longer able to connect to the receptor and its psychoactive properties go down. That is, according to scientific terminology CBD is non-competitive negative allosteric modulator of CB1 receptors.
Under the second, more complicated explanation, CBD inhibits the enzyme that make THC active.
If you are one of those who like reading medical instructions, you have probably noticed in the section on interaction with other medical products references to cytochrome-450 that is inhibited by drugs (dampens or competitively inhibits). Its function is oxidation of many substances, specially fats that are afterwards easier to dissolve, decompose and filter by kidneys. Thus, inhibition of cytochrome-450 usually means growth of other drugs concentration in blood and accordingly their stronger effect, which even can be equivalent to overdose.
Yet in case of THC it happens just the opposite as in oxidated form (11-OH-THC) it works several times more actively. So when CBD inhibits cytochrome-450, psychoactive effect declines.
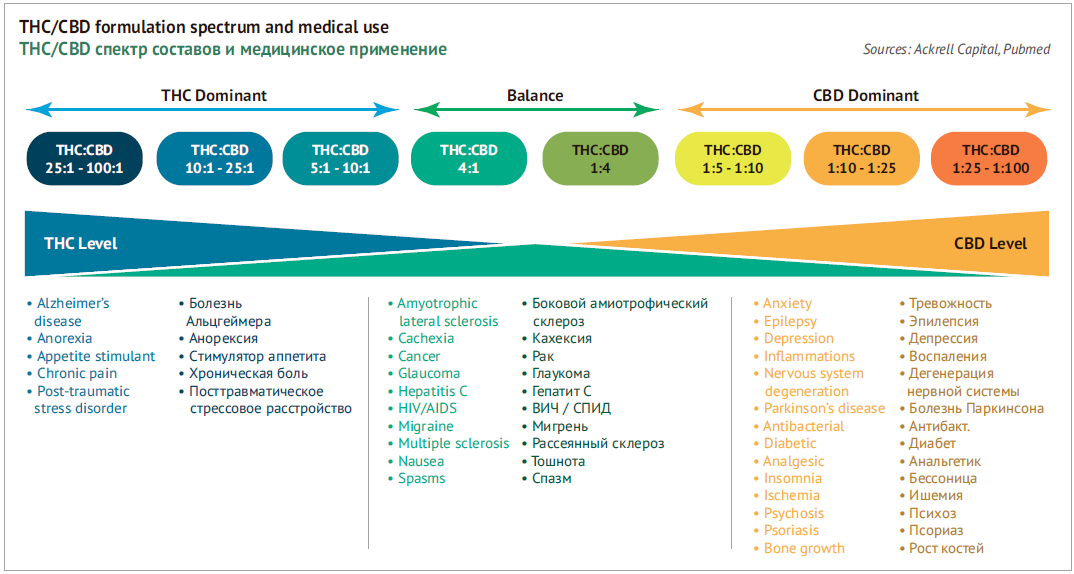
It is interesting that in many medical applications, TCH is less effective without CBD. For example, when using THC as a pain-killer, in treating oncological diseases, or in some forms of epilepsy.
Currently new sorts of cannabis (and cannabis-based products) are being developed with various THC/CBD proportion and various properties balance.
It is well-known that tea contains a stimulant, caffeine. There is 1.5-2 times more caffeine in green tea than in black tea, yet even it would be enough to experience stimulating adrenalin-like effect. However, tea, especially green one is considered to be a neutral drink due to substances compensating for the psychoactive effect.
One of such caffeine “compensators” is theanine that is a psychoactive substance and can come through blood-brain barrier. Thanks to similarity to stimulating neurotransmitter glutamate, theanine blocks glutamate receptors of the brain and raises the level of inhibitory neurotransmitters. And people’s mood rises as well as cognitive functions, while physical and psychic stress decreases.

But beside the brain, you can find glutamate receptors on human tongue. So, theanine gives green tea specific for drinks “umami” taste which is easily differentiated by Asian consumers and poorly by European ones.
This is the taste of protein-rich substances which is clearly felt in broth, cheese, fried meet, other products and food additive sodium glutamate. Umami makes up a separate fifth taste in China, Japan and other countries of Far East. Perhaps that is why, theanine is allowed and widely known as a food supplement in conservative Japan (and the USA), but not allowed in the EU.
As we can see, huge popularity of tea is to a great extent connected to its tonic effect – by complicated balance of agitation and inhibition which results from caffeine, theanine and other substances action on nervous cell receptors.
Cannabis status
Legalization, decriminalization or tolerance?
The official status of cannabis can have several levels. At the level of zero tolerance, consumption of any cannabis product for any purpose is forbidden (even non-psychoactive medical substances for ill people) and liable for prosecution. At the maximally liberal level adult people can without any legal responsibility use cannabis not only for medical purposes but also for recreational (that is just to get pleasure).
The transient position between fully illegal and legal status is decriminalization. The difference between them can be described in the following way:
1) Legalization of cannabis: is the process of removing all legal prohibitions against it. Cannabis would then be available to the adult population for purchase and use at will, similar to tobacco and alcohol.
2) Decriminalization of cannabis: is the process of removing criminal sanctions for cannabis use, which would still be illegal. Normally the legal system would not prosecute a person for possession under a specified amount, though production and sale would be strictly forbidden. Sometimes administrative measures are possible – fines or enforced measures to restrain consumption.
 Under condition of easy accessibility, decriminalization and social tolerance of cannabis are much more important that its official legalization. American researchers* comparing data on students’ polls with different status of cannabis arrived at a conclusion that removing moral barriers and legal consequences are main preconditions for consumption growth.
Under condition of easy accessibility, decriminalization and social tolerance of cannabis are much more important that its official legalization. American researchers* comparing data on students’ polls with different status of cannabis arrived at a conclusion that removing moral barriers and legal consequences are main preconditions for consumption growth.
* Commentary on «The impact of the legalization of recreational marijuana on college students». Addictive Behaviors 77: 2019
Here we can give two examples. In the Netherlands, a country famous for maximally tolerant attitude to cannabis it is not legalized but decriminalized due to widely known “tolerant policy”. At the same time official decriminalization of cannabis in Russia (only an administrative fine is stipulated for 6 grams of weed) very often means serious consequences for an inflictor.
Officially in practice legalization and decriminalization of cannabis can be carried out by various schemes.
1) Can be the result of direct democratic processes and contacts of government and society in the form of petitions, referendums or polls (some states in the USA and current processes in Luxemburg and New Zealand).
2) This can be a state’s higher court decisions basing on applications from public organizations, juridical precedents and others (Canada, SAR, Mexico, Georgia, Costa-Rica, current processes in India).
3) This way a state can solve problems of criminal turnover of cannabis and organized criminality (Uruguay and the Netherlands). In case of Uruguay, decriminalization took place even against the opinion of the population majority.
4) Pharmaceutical companies basing on scientific data of medical researches are trying to achieve the government’s permission to THC usage for medical purposes (Great Britain). The medical use can open the gate for further legalization of recreational consumption. In Saint-Vincent and Grenadines the legalization took place after consultations with business and agricultural producers.
What WHO recommends to UN
At the international level the status of cannabis is regulated by Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of UN in 1961. This many-page document that was signed by virtually all countries of the world in order to develop general policy and international control of drugs. The convention contains 4 lists of addictive drugs depending on the danger and strictness of control.
The structure of lists is a little confused but we can say this way – all substances with known narcotic effect (either weak or strong) are included in comprehensive list I, and some light opioids belong to short list II. These two lists form two more lists. List III contains pharmaceutical means with mitigated control and list IV consists of drugs with the strictest control that must not be used for medical purposes as for example heroin.
Today list IV also includes tops of plant cannabis and resin obtained from it. The notes mention tinctures, cannabis extracts and Sativex drug, as well as formulas for counting substances in cannabis equivalent.
Let us note that beside Convention of 1961 on addictive drugs, there is also Convention on psychotropic substances of 1971 which enumerates chemical compounds. There the focus is shifted from cannabis to psychoactive substance – THC. The convention of 1971 also includes charts with different control levels but it admits that THC can be beneficial for medical purposes.
The status of addictive substances can be changed only in case when the World Health Organization obtains new important information concerning them. As a rule it takes place due to pharmaceutical companies’ activity, representatives of certain countries or public organizations. The general director of WHO addresses UN’s general secretary who brings recommended amendments for voting to special committee CND we will tell about below.

From the beginning, general director of WHO in his/her propositions relies on Experts’ committee on drug dependence (ECDD WHO). It is an independent group that analyzes the global situation from the point of view of drugs use.
ECDD experts compare risks for health and benefits from use of psychoactive substances basing on three main criteria: 1) dependence development, 2) facts of misuse and 3) possibility for medical use.
In 2016, ECDD experts paid attention to the fact that ever more states (violating the Convention) allow cannabis for medical and non-medical purposes and there appears more and more proofs for its impact on health. However, cannabis has never been under the committee’s observation because of the lack of reliable scientific data.
The status of cannabis as an addictive drug from IV list with the biggest risks and lowest benefits demanded the experts’ revision. Yet, potential change of cannabis place in Convention lists can significantly expand pharma companies’ and scientists’ possibilities for scale researches and application at national levels.
So WHO initiated the process of scientific estimation of use (medical or other) and potential harm from plant Cannabis sativa and its derivatives. Researches by leading scientific experts in chemistry, pharmacology, toxicology, epidemiology and therapeutical application have been commissioned.
In summer 2018, ECDD experts decided they had enough information for critical look at cannabis. At that time already, they arrived at the conclusion that cannabidiol (CBD) should be excluded from the convention on addictive drugs as it does not have any psychoactive properties and does not develop dependence.
The final, so called critical survey was carried out at summit of ECDD in November 2018. In conclusion the experts recommended:
1) Remove cannabis and tar from the strictest list IV of addictive drugs.
2) Introduce THC and its isomers in the general descriptive list I of addictive drugs.
3) Exclude extracts and liquors of cannabis from descriptive list I.
4) Remove international control of CBD containing less than 0.2% THC.
5) Include THC into list III of addictive drugs allowed for medical use, that is in less strict control list than with the current status of cannabis.

Though conclusion of a big group of experts cannot be subjective, the possibility to improve the international status of cannabis arouses mixed reaction. Since the cannabis status as a very dangerous drug is fixed in the legislation of many countries, its change would imply the admission that the previous judgment was wrong and a transient victory of the legalize party which seems revolting to conservative authorities as well as a part of society.
In 2018 the situation was acutely politicized due to legalization of recreational-use cannabis in Canada. Viroj Sumyai, head of the UN’s International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) stated than that it contravened the key International Drug Control Convention, and is “not a healthy” lifestyle choice. Official representatives of Russia and China expressed a special concern on this issue stating that recreational cannabis consumption for the health protection and population welfare is a misconception that can ruin the international narcotics control.
Canada representative responded that his country has been consistently fighting with illegal drug traffic, besides, according to the second part of Convention of 1961, a country is to take decision on the most appropriate means of population health protection, basing on the current situation.
No wonder that the international opinion conflict has complicated the cannabis status reconsideration.
The decision will be taken by UN’ international Committee on narcotic drugs (CND) which is elected for four years and consists of 57 countries. Their members change each time but it is balanced by regional groups (constant number of representatives from Asia, Africa and so on). It is CND that allocates narcotic drugs by lists I-IV of the Convention or change their status taking into consideration critical compulsory researches by WHO and ECDD experts’ specialists.
As early as in March 2019, CND could have adopted amendments concerning cannabis, yet it was decided to postpone the voting date, officially due to delay in presenting materials of ECDD research. Though some representatives (from Norway and Uruguay) spoke for immediate decision, the most of regional groups (including representatives of Japan, Russia, USA and Germany) stated it was a complicated issue that demanded more time and consultations with WHO. Besides there rose questions on acceptable quantity of THC in CBD medicines and application of cannabis medicines. It is quite possible that the amendments will be brought back for voting only at the beginning of 2020.
Basing on the position of the most conservative countries, there can be formal steps in UN and declarations that production and wide application of cannabis is possible but only for medical and scientific purposes while the recreational cannabis use is still unacceptable. Such collective steps can ease the situation and create preconditions for changing the Convention lists and allowing pharmaceutical products of cannabis into the markets. One more scenario is foot dragging and constant postponing of CND voting, which is quite possible if most of the committee members decide to further maintain the status-quo.
Global market of cannabis
Consumer’s profile
The cannabis issue is gaining publicity due to young generations, who have created their own view on the consumption. For them, the opinions and rules consensus as to cannabis formed in 1940-1970 is not something taken for granted and look archaic.
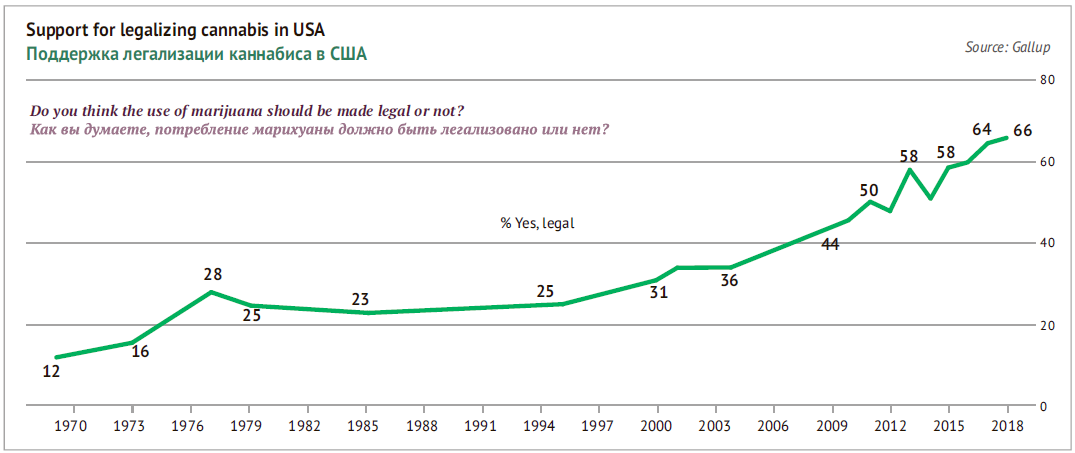
The general approach to products of people aged 19-35 is now formed not so on opposition to previous trends as on seeking for bold and functional innovations, a very critical attitude to information as well as on serious approach to health and life quality. They do not watch TV (nor TV advertisement) and learn about products qualities from search engines, from blogs or “friends” on social media. They are interested in new and personal consumption experience, lifehacks one can share. The new generations consume little alcohol, smoke vapes instead of cigarettes, choose craft products instead of industry ones, prefer nonconforming styles to pop-music…
Such attitude to life, information and products has resulted in rapid formation of cannabis-loving community in tolerant countries. Cannabis has recently started entering the legal field, so its consumers felt united by the air of taking part in illegal, funny, and anticorporate action.
Cannabis consumers can be divided into three conventional groups that do not have distinct borders: heavy recreational, light recreational and medical.
 Loyal (heavy) consumers are used to illegal consumption. They are sure in wholesomeness and safety of cannabis and that it is a victim of politicians’ plot that need workers and soldiers and do not need happy and independent people. The plot is also made by Big Pharma (pharmaceutical giants) and sometimes alcohol lobby that is doing its best to suffocate the competitor. Countercultures of reggae, hippy, rap and Indie strengthen the alternative and freedom-loving image of cannabis consumer. Consumerism and carrier race are opposed to relaxed lifestyle of Big Lebowski.
Loyal (heavy) consumers are used to illegal consumption. They are sure in wholesomeness and safety of cannabis and that it is a victim of politicians’ plot that need workers and soldiers and do not need happy and independent people. The plot is also made by Big Pharma (pharmaceutical giants) and sometimes alcohol lobby that is doing its best to suffocate the competitor. Countercultures of reggae, hippy, rap and Indie strengthen the alternative and freedom-loving image of cannabis consumer. Consumerism and carrier race are opposed to relaxed lifestyle of Big Lebowski.
 ОYet one should not take the protest too literally. Both Bill Clinton and Barak Obama smoked cannabis (though the first one did not inhale) which did not stop them from making their carriers. As social polls show in the USA* the majority consists of light consumers. For them cannabis is not so much a riot as a zesty spice to their modern daily life. Many of them go in for sports and fitness and take cannabis as a healthy product helping to restore after job and work-out. Some parents even entertain themselves with cannabis during their parental leave. Foodies study food properties of cannabis and terpene profile of different sorts. Other key interests include: travelling, technologies, nature, yoga and fashion.
ОYet one should not take the protest too literally. Both Bill Clinton and Barak Obama smoked cannabis (though the first one did not inhale) which did not stop them from making their carriers. As social polls show in the USA* the majority consists of light consumers. For them cannabis is not so much a riot as a zesty spice to their modern daily life. Many of them go in for sports and fitness and take cannabis as a healthy product helping to restore after job and work-out. Some parents even entertain themselves with cannabis during their parental leave. Foodies study food properties of cannabis and terpene profile of different sorts. Other key interests include: travelling, technologies, nature, yoga and fashion.
* «Cannabis Consumers», Brightfield Group
 The third and separate group of consumers joined by common interests is formed by people having health problems. They are often interested in non-psychoactive CBD and remain members of international internet communities. These are very motivated and serious people faced with difficult situations: 1) people ill with severe diseases or their relatives, 2) parents of children with steady neurological disorders, 3) people with chronical disorders who do not feel better after traditional prescribed drugs and supplements and so on. They are as loyal to cannabis as much hope they have in it or help in treatment they actually get.
The third and separate group of consumers joined by common interests is formed by people having health problems. They are often interested in non-psychoactive CBD and remain members of international internet communities. These are very motivated and serious people faced with difficult situations: 1) people ill with severe diseases or their relatives, 2) parents of children with steady neurological disorders, 3) people with chronical disorders who do not feel better after traditional prescribed drugs and supplements and so on. They are as loyal to cannabis as much hope they have in it or help in treatment they actually get.
Naturally the key interests of such consumers are connected to dosage patterns, cannabinoid forms, various brands, responds to treatment and ways to buy cannabinoids in the countries where it is illegal. The intersection region of this audience and recreational consumers is not very big and usually linked to cannabinoid consumption against widely-spread social illnesses such as depression, stress, anxiety, insomnia and others.
As we have already noticed compared to other psychostimulants (alcohol and drugs) cannabis involves disproportionally many young people under 35 – starting from senior high school students to junior specialists. A small layer of adult people contains mainly experimentalists, representatives of specific cultural communities and creative professions. As experience shows, legalization sometimes attracts some more conservative people of the middle age to the market, yet there are not many of them, and usually they are light consumers who have consumed cannabis in their youth.
Patchwork quilt
In 2016, the share of cannabis consumers amounted 192 mln people by WHO data. Let us consider their distribution by regions*.
* The consumption assessment is very rough and based on data by WHO and EMCDDA as well as on expert estimations that can differ by several times. We do not have reliable data on cannabis tolerance in 100 countries mostly African and small island states where nearly 10% of the planet’s population live and cannabis is officially forbidden.
In particular, about 23% of consumers live in Asia, Near East and North Africa, where exists a de-facto tolerant attitude to unpublic recreational consumption of cannabis on behalf of controlling authorities and society though officially cannabis is forbidden and not decriminalized.
As a rule these are countries with warm climate where one can easily get psychoactive sorts of cannabis that grow naturally or are illegally planted for contraband (including those with high content of THC). The most of these countries belong to developing ones and have a dense population. Obviously, regardless of their economic position and state regulation in the nearest future the legal trade of cannabis is not likely to prevail over illegal one as it will resemble selling ice in Alaska.
In the belt of Islamic countries from South-East Asia to North Africa such as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Iran, Egypt, Morocco and Nigeria. They are at the same time the major cannabis providers to European market.
Buddhist countries of South-East Asia with rather tolerant attitude to cannabis are Thailand, Nepal, Cambodia and Laos.

India has a special position in Asia as 17% of global cannabis consumers live there. India stands out not only for the scale but also for the potential of gradual legalization as cannabis is a part of some Hindu rituals. Its consumption is differently regulated from state to state but society (especially the young generation) has almost the same attitude to cannabis as to alcohol.
The remaining 77% of consumers form a commercial group who buy imported or hydroponic cannabis in the black or legal market. Basing on the average consumption frequency (twice a week at the average) and average expenses for cannabis or products with THC (nearly $6.4) one can quite approximately estimate the global legal and illegal cannabis market at $100 bn in 2016 (for comparison, the global beer market is estimated at $580 bn). Let us note that by 2018 the cannabis market has grown due to increase of consumers’ number and higher consumption frequency.
7% of consumers live in nearly 100 countries with conservative legislation and negative attitude to cannabis in the society. The bulk of these countries form a wide belt from Poland to Singapore.
The cannabis tolerance is low here due to absence of deep consumption traditions and strong influence on various spheres of life on behalf of the state or due traditional self-regulation by the society. These are many Asian countries: China, Vietnam, Indonesia, Japan, the Philippines, Myanmar, South Coria, Singapore; Russia and most post-soviet or post-communist countries, many Arab countries with high per capita income level and others. In the foreseeable future buying cannabis and THC products in these countries will remain illegal even for medical purposes.
70% of cannabis consumers from nearly 50 countries live in the regions with legal sale of cannabis, potential legalization or tolerant atmosphere. They can have a relatively free and safe access to cannabis or THC products just for pleasure or by traditions. Half of worlds’ population lives in these countries.
10% of these consumers of cannabis are in the legal field today already. There are six countries where recreational consumption use of THC products is legalized namely Uruguay, Canada, SAR, Georgia, the USA (ten states) and Spain (Catalonia). And in these countries there are a lot of conditions, such as age, maximum THC content, ban for foreigners, consumers’ club membership and so on.
Approximately 25 countries where recreational use of cannabis is decriminalized can be divided into two groups.
The first group includes countries, with generally liberal state regulation, this is almost a half of EU (the Netherlands, Italy, Belgium, Czech Republic, Portugal, Croatia, Slovenia, Estonia, Luxemburg and Malta) as well as Israel and Australia (certain states).

The second group is formed by most Latin America countries where the state has adapted laws to therapeutic use of cannabis and does not strive to strongly influence the entertainment sphere: Mexico, Columbia, Argentine, Peru, Chili, Ecuador, Bolivia, Paraguay, Costa-Rica, Belize, as well as some of island Caribbean countries, Jamaica, Antigua and Barbuda and Bermuda.
Mexico, Germany, Luxemburg, Dania, Greece, Italy and Malta are underway of creation a legal and regulated cannabis market or actively discussing this possibility.
Legal market of cannabis
Presently the bulk of the global cannabis market is illegal and associated to recreational consumption. But as it enters the legal field the market is growing dynamic and multidimensional. There is an emerging medical segment, certain categories form big markets of pharmaceuticals (THC or CBD) as well as non-psychoactive products with CBD.
Under analysts’ estimations at Arcview&BDS in 2018 the global legal market of cannabis* runs at $12.3 bn. Basing on our estimated data, in 2016 the share of legal cannabis sales in the total volumes corresponds to 6%, and could have increased to roughly 11% by 2018. The legal market has a huge growth potential both at the expense of illegal market and due to cannabis consumption growth.
* Not taking into account products with CBD and pharmaceuticals.
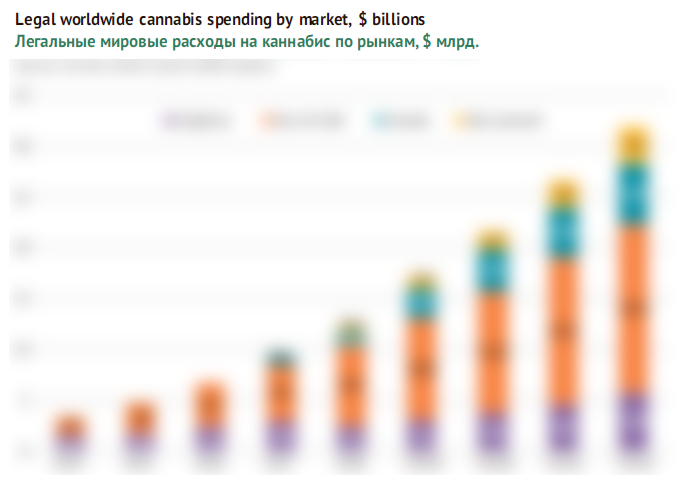
In the structure of legal sales, the USA with their $10.5 bn turnover is an absolute leader (New Frontier estimates the illegal market at $26.8 bn.) The second place is taken by Canada with a legal market of $1.2 bn.
According to analysts’ prognoses, cannabis sales in the USA will continue growing rapidly, yet the dynamics of the global market will be provided by Canada and other counties. By 2022 the volume of the global legal market of cannabis will double and reach $22.2 bn. Later there is expected a qualitative increase of sales in the USA provided FDA regulates THC consumption at the federal level and companies obtain a new impetus for investments.
In 2019 a boom of cannabis and industrial hemp production is expected in North America as license farmers are expanding acreage. This means further price decrease for cannabis. One can also expect further liberalization of legislation and developing easy game rules, as the current policy of the USA is directed at supporting the agriculture.
Californian case
The decline in California is very significant as a good example of obstacles in transiting from limited medical to more market-ruled but still regulated consumption.
The legal market of cannabis is a small part of the general market. Shadow dealers in case they have such chance will rapidly take away sales from legally working sellers. That is exactly what happened in the world’s biggest legal cannabis market in California, when in 2018 the volumes there fell by 20%. Further rapid growth in the USA took place in other comparatively not bid states, Colorado, Washington, Oregon and some others.
Recreational use of cannabis was approved by California’s people at a referendum in 2016. The authorities expected that during several years after the law came to force, there would be 6000 licensed cannabis dispensaries. Before transiting to license sales system, there were 1790 medical cannabis dispensaries and it seemed that the trade structure would be rapidly scaling.
Yet, there was mildly saying no riot growth of outlet number. As of the third quarter of 2018, there were only 455 cannabis outlets (dispensaries) in California. 12% of them have a license for selling medical cannabis, 4% for recreational and 84% for the both purposes.
It turned out after the legislation change the medical cannabis outlets are experiencing a big tax and organizational pressure and get four times less profit than recreational cannabis outlets. However, the recreational segment faced a huge tax load and unexpected approval difficulties as well as locals’ and authorities’ resistance to outlet opening.
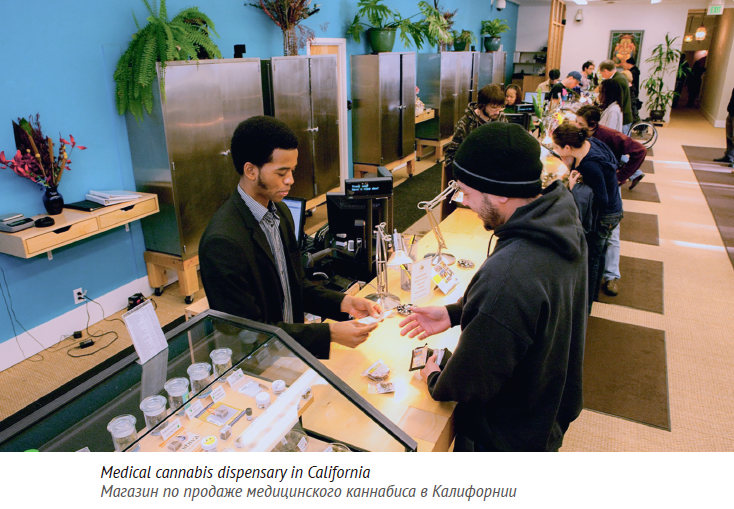

The license sellers could not compete with illegal markets either in price or distribution. As a result, instead of a regulated medical system of cannabis sales there appeared ruins and a lot of puzzled entrepreneurs.
Seller’s prices of legal and illegal cannabis producers in the recent years have gone down considerably due to competition. But in California only illegal dealers took advantage as their retail trade have also decreased while at the legal sellers the prices increased due to taxes that make up not less than a third of the retail price.
Besides, the small number of outlets makes the life of legal consumers more complicated. In most of small Californian cities the locals voted against cannabis sales in their territories. Only 89 out of 482 cities allowed cannabis sales, however, the majority of population lives in these cities (Los-Angeles, Oakland, San-Francisco, San-Diego and others). The problem was aggravated by demand to the seller to check cannabis shipments for pesticides.
Despite all these difficulties, the system of sales has started to come to order little by little and in the third quarter of 2018, the legal market started growing. Official sellers managed to persuade buyers in their responsibility, turned to branding and marketing technologies, expanded their product range and improved service. It is expected that in 2019 the legal market will at least restore its positions.
Segment of medical cannabis
The tradition of cannabis consumption for medical purposes interrupted in the 60-ies of XX century as it was included into Convention in 1961.
No sooner than in 1991 in California and later in other states of the USA, locals managed to influence the authorities by referendums demanding to allow cannabis treatment of sever illnesses. Currently there are only three states, where medical cannabis is illegal (Idaho, South Dakota and Nebraska). Yet it is unlikely that FDA will legalize and approve medical consumption of cannabis and THC at the federal level because of conservatism, long terms of clinical trials, opposition from Ministry of Justice and Anti-drug Agency. In the nearest future, laws on cannabis use for medical purposes will be adapted basing not on scientific data and medical practice but on the public opinion.

Following the USA, the progress was achieved in 23 more countries that allowed legal consumption of cannabis for medical purposes. These are Canada (1999), Israel (2001), the Netherlands (2003), Switzerland (2011), Czech Republic (2013), Australia (2016), Turkey (2016), Germany (2017). It is allowed to get cannabis treatment in many countries of Latin America.
Several EU countries created special access schemes to cannabis treatment for narrow spectrum of diseases (Croatia, Denmark, Finland, Norway, Poland and Sweden).
As far as we know, 14 countries are in the legalization process of medical cannabis and THC products: 4 countries of South-East Asia (India, Japan, Philippines, Thailand), 8 countries of EU (Lithuania, Belgium, Ireland, Iceland) as well as New Zealand, Ukraine and Jamaica. It is possible that there are more of such countries.
In nearly 25 other countries recreational cannabis is de-facto accessible, in case people on their own without consulting with a doctor decide to use it for medical purposes.
The market of medical cannabis is well-developed in America where it in many aspects overlaps and interacts with recreational market.
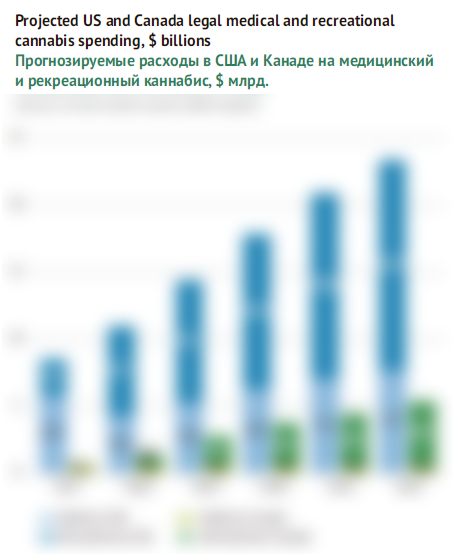
At the largest USA market according to Arcview&BDS estimations in 2017, the legal sales of cannabis for recreational use amounted to $2.6 bn, and $5.9 bn for medical use. In 2018, due to reformation and problems at Californian market, this proportion was sharply changed in favor of recreational use (6.7/4.3). According to conservative prognosis by analysts, the rates of the legal medical consumption of cannabis will be much behind the recreational one, but will still be high, thus by 2022 the medical segment can grow by 80% to $7.7 bn.
Clinical trials of cannabis in the USA is regulated at the federal level and till 2015 they were virtually blocked. Doctors when they prescribe cannabis drugs are often obliged to comply not with norms confirmed by research data, but with existing laws.
 After legalization of recreational consumption in Canada, it gradually achieved the level of the medical ones and even exceeded it a little. In the future, Arcview&BDS analysts do not expect any sales growth in the medical segment, they will stay at the level of $0.6 bn despite the prognosed four-fold market growth of medical cannabis by 2022.
After legalization of recreational consumption in Canada, it gradually achieved the level of the medical ones and even exceeded it a little. In the future, Arcview&BDS analysts do not expect any sales growth in the medical segment, they will stay at the level of $0.6 bn despite the prognosed four-fold market growth of medical cannabis by 2022.
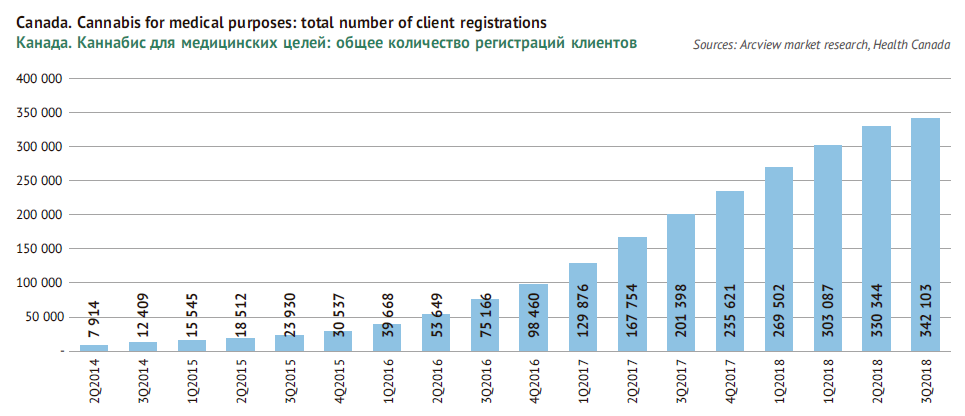
Interestingly, the medical segment itself in Canada has developed very quickly. While by the beginning of 2015, there were 18.5 thousand patients who got a prescription for cannabis from their doctor, by the beginning of 2018, their number reached 300 thousand (0.8% of Canada’s population). After getting the prescription, the patient can buy cannabis at a seller with a federal license, grow a limited number of plants at their own land or choose any other man who can grow it.
According to report by Brightfield Group analytical company in EU cannabis markets and their products can grow exponentially during the next several years and legal sales of cannabis will grow from $316 mln in 2018 to almost $8 bn to 2023. In particular the largest European market of medical cannabis, German, can grow from $73 mln to $2.7 bn. Great Britain and France have the biggest growth potential as 1) regulation weakens and new sales channels 2) the area of medical use of cannabis expands.
Only in 2018 in the territory of EU cannabis industry has received 0.5 bn euro under the estimation of specialized research company Prohibition Partners. According to their opinion, if all EU countries legalize medical cannabis and create a developed trade infrastructure, less than in ten years the market will grow to 115 bn euro (and this is roughly the volume of the beer market of EU today). Complete legalization of only medical consumption will mean cannabis market growth to 58 bn euro.
THC Pharmaceuticals
Along with the legal, yet poorly regularized market of medical cannabis, the segment of licensed pharmaceuticals with psychoactive cannabinoids is actively developing today. Due to problems with using plant materials, synthetic analogues of THC were the first to appear at the market: Nabilone (drugs under brands Cesamet and Canemes) and Dronabinol (by Marinol and Syndros).
 The legislation liberalization in most of countries led to rapid expansion of Sativex drug of herbal origin THC. It is manufactured by GW Pharmaceutical company that was registered in Great Britain in 1998 and got a license for cannabis growing from Ministry of Internal Affairs for scientific purposes, which made it one of pioneers of medical use of cannabis.
The legislation liberalization in most of countries led to rapid expansion of Sativex drug of herbal origin THC. It is manufactured by GW Pharmaceutical company that was registered in Great Britain in 1998 and got a license for cannabis growing from Ministry of Internal Affairs for scientific purposes, which made it one of pioneers of medical use of cannabis.
Naturally, taking such drugs mostly lies in the legal field they are under restricted access in most of the countries of EU (except for Bulgaria, Greece, Cyprus, Lithuania, Romania and Slovakia).
Yet, the accessibility of medical substances depends not only on legalization but also on protocols, doctors’ wishes and abilities to give prescriptions as well as on existing distributional system. The price for licensed drugs can be very high. So, at many markets the situation looks multivalued.
One of bright examples is Philippines where medical drugs of cannabis are not prohibited official but there has been only one case when a patient managed to overcome all obstacles and get the approved drug with THC. However, president Duterte in the nearest future intends to improve this situation.
We have not found data on the scale and potential of cannabis-based pharmaceuticals market but the rapid expansion of the material base judging by slightly outdated reports of 2018 by INCB.
Thus, since 2000, more and more countries have started to use cannabis and cannabis extracts for scientific and medical purposes (which probably means deep processing of cannabis for production of pharmaceuticals). In 2000, the total volume of legal production was 1.4 tons. In 2016 it doubled against the previous and increased to 211.3 tons. By that moment, the industry was dominated by Great Britain with a share of 45% and Canada with 38%, that along with Portugal made the biggest contribution into the volume growth. The share of Israel was decreasing as the output volumes though increased, were behind the competitors.
CBD: Rocket market
Regional status
As a product of cannabis processing, non-psychoactive CBD often faces official limitations in turnover regulation. Currently there is a revision of CBD status is in progress which is based on objective data. Yet despite WHO conclusion of CBD safety, the regulation of its status is delayed by politicians’ conservatism, business interests of pharmaceutical companies and absence of normative base at regulating authorities that have to transit to differentiating assessment of cannabis products basing on the chemical elements on the contents.
In conservative countries with rigid legislation CBD belongs to cannabis extracts and is equally rigidly limited. The legislation often gives CBD the status of the strictest list IV by international convention. In some countries where CBD is legal its consumption and sales can be severely regulated by the rules of pharma market (that is, it has to be a licensed drug prescribed by a doctor).

However, in practice in most countries of the world it is not difficult to order imported products with CBD (normally produced in the USA or EU) not expecting any legal consequences. The range of producers and brands is huge, only in the USA their number approaches a thousand. There are about two hundred of manufacturers of CBD-containing products.
Paradoxically, CBD popularity in treating many diseases and hard severe conditions is poised to widely spread CBD. The effectiveness of CBD is still not confirmed scientifically (years are needed for this), yet it is very actively discussed on the net among people who have health problems.
Over the recent years, the world image of CBD has been slightly damaged by warnings that FDA issued to many food supplements producers. Firstly, the agency demands to stop promising healing severe diseases and in general advertise the supplements with CBD as medical production. Secondly, they demand to mark products correctly (some of the companies even spelt “cannabidiol” and “inflammation” with mistakes). Thirdly, sample purchases showed that CBD content in many supplements is considerably lower than stated and in some samples heavy metals and pesticides norms were exceeded. Fourthly, there have been cases of fakes revealed.
Besides, voluntary use of non-licensed supplements opposes medical practice of prescribing substances with a definite dosage and dosage regimen, degree of purification, form, etc. The comparatively low price of food supplement with CBD evens research, registration and marketing expenses by pharmaceutical companies. So FDA and some other countries’ regulators lobby CBD registration as a medicine.
Besides, there is a problem of different hemp sorts control and maximum THC content in the final product. Though common industrial hemp with low THC content can be a source of CBD, for decreasing production costs and getting qualitative product it is much more effective to use specially selected sorts of cannabis. Naturally, industrial planting and such sorts turnover demands development of legislative base.
In order to learn the status of cannabis at the regional market not going into too much detail, it suffices to find out whether official dealers and CBD-products manufacturers work at the market and who they are: pharmaceutical companies or supplements and health products suppliers.
Let us briefly discuss the situation at the regional markets.
In European Union cultivation of Cannabis sativa sorts is allowed under the condition that the sort is registered in General catalogue of agricultural plants of EU and THC content does not exceed 0.2%. This means that it is not forbidden to produce cannabis with a high content of CBD. Yet, the key issue is the definition for the “new product”. While hemp seeds, hemp seed oil and hemp flour are well known and have a history of consumption, CBD belongs to “new products”. In this case, whether a product belongs to foods, is determined by the national legislation of each country. Due to the principle of mutual recognition, any country of EU, where CBD is defined as a food product, can export it into another country and sell at the local market provided the national legislation does not directly forbid its sales.
Supplements with CBD can be legally bought in most EU countries. Except for Spain, Denmark, Slovakia and Malta where CBD is a drug, so one needs a prescription from a doctor to buy it. In Spain sellers did not have serious problems until last autumn when the police started raiding and confiscating production because of nonconformity to demands to food supplements (there is simply no such demands for CBD). In Denmark the situation is similar, yet there are official explanations for ban on food supplements with CBD.
Besides, CBD is still illegal in the market of Slovakia because of juridical confusion in registration it as a psychotropic component of Sativex also containing THC. However, it is not difficult to find firms that sell CBD at the local market.
 In China CBD is manufactured by Hanma Investment Group. It is the only legal investment company in China that controls the whole chain – from hemp growing to producing biopharmaceutical drugs (via subsidiary Hansu Biotechnology). As far as we know at the moment cannabinoids are supplied for medical purposes to medical institutions and for military purposes (for instance production of pain-killers). However, the company is certain in wonderful outlooks for CBD at the Chinese market of FMCG. Hanma Investment Group is also known as one of the world’s biggest CBD exporters.
In China CBD is manufactured by Hanma Investment Group. It is the only legal investment company in China that controls the whole chain – from hemp growing to producing biopharmaceutical drugs (via subsidiary Hansu Biotechnology). As far as we know at the moment cannabinoids are supplied for medical purposes to medical institutions and for military purposes (for instance production of pain-killers). However, the company is certain in wonderful outlooks for CBD at the Chinese market of FMCG. Hanma Investment Group is also known as one of the world’s biggest CBD exporters.
In India one can buy supplements of local production as well as licensed imported pharmaceuticals. Though in each of India’s 36 territorial entities its special rules and restrictions can be acting.
In the market of the USA there is a federal law on farming enterprises signed by president Trump, stipulating that CBD is legal if manufactured from “industrial hemp” containing up to 0.3% THC (the same concerns imported “non-psychoactive hemp”). Such CBD products were approved by FDA and they are currently available on the net virtually everywhere in the country. Yet the market outlooks are uncertain.

American subdivision of British pharmaceutical company GW Pharmaceuticals lodged an MA application for Epidiolex drug which contains CBD isolate. This led to prohibition of CBD-containing supplements from FDA in order to regulate medical application and stimulate pharmaceutical companies to carry out medical researches. Yet the state level legislation allows selling supplements and a federal law on cannabis and cannabinoids of 2018 that can put all the things right having finally clarified the legal status of supplements with CBD draft is currently under consideration. A lot of congress members as well as American industrial companies support this. Compromise will be most probably found in the sphere of marking and limitations of maximum CBD concentration in the final enriched product.
In Canada CBD status is slightly paradoxical as its regulation is connected to cannabis status. After the recreational consumption was legalized, products with CBD are allowed to be bought at the same grounds. Prior to that only registered medical patients with prescriptions could legally buy licensed CBD. Supplement producers are actively trying to include CBD into the list of natural health products yet experts of medical cannabis and pharmaceutical companies oppose to it. However, consumers wishing to buy CBD without a prescription will not have serious difficulties with it.
In most countries of Latin America, where the attitude to cannabis is tolerant, supplements and drugs with CBD can be bought legally.
Until now, in the majority of conservative post-communist and Islamic countries CBD is considered a precursor of narcotic substance, and its regulation is formally joined with them under the same umbrella of cannabis. Even in those hot countries of Asia and the Near East, where sort Indica is illegally and widely consumed, there are sometimes problems with purchasing CBD and not numerous consumers smuggle it.
CBD market
Medical properties of cannabidiol have been discussed in chapter “Almost a panacea”. But the excellent outlooks of the wildest CBD application are based not so much on disease treating as solving common personal and social problems: decreasing anxiety, insomnia and stress, preventing age disorders and stopping inflammatory reactions. And CBD is not necessarily used with THC, it is effective as it is.
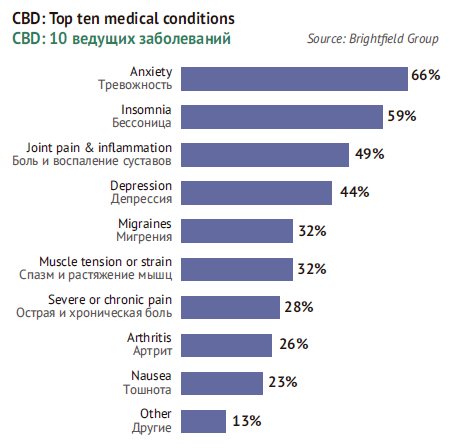
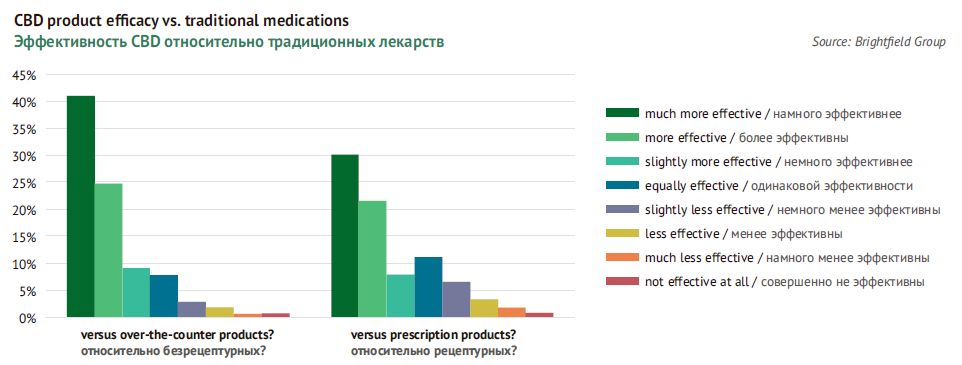
By conducting regular polls of USA consumers, Cowen Research’s analysts to their surprise found out that as of January 2019, as much as 7% of respondents reported they used CBD. Those who want to have a deeper insight into this target group, should also have a glimpse at Understanding Cannabidiol published in 2017 by Brightfield Group. In particular, 52% of respondents consuming CBD said that it turned out to be either more effective or much more effective for treating their diseases than drugs prescribed by their doctor. Only a very small part of respondents said CBD was slightly or not effective at all.
Cannabidiol market can be divide into three main segments.
The first segment is products with CBD for health and wide application that are produced from stems and leaves of industrial hempwithout inflorescences. As a rule CBD content of such products is not high, that is, about 3.5% and THC volume is strictly regulated and does not exceed 0.3%.
As cannabis technical derivatives are usually free from specific limitations, they are the most widely spread at the market. In the USA the sales volume of hemp-derived CBD in 2018 was rated at $264 mln by New Frontier’analysts. By 2022 the market can grow by 2.5 times comparatively to $646 mln.
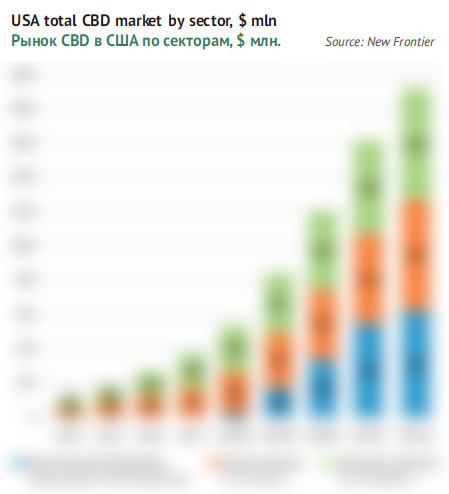
The second segment consists of the same health and wide application products with CBD, yet obtained from cannabis plantswith oily inflorescences that are rich in cannabinoids. Often, even in selective sorts of cannabis rich in CBD, there is also some percentage of THC. Unlike the products of industrial hemp, products form cannabis have usually higher concentration of CBD and therapeutical effect.
In the USA the market share of this category amounts to $240 mln, that is, much less than hemp CBD market. Yet it is expected by analysts that in 5 years the shares of these categories can get equal.

The third segment – licensed and approved for selling pharmaceuticals with CBD. Among them we can point out Epidiolex by GW Pharmaceuticals (like Sativex it contains THC). The key event for the company was completion of long process of FDA approval and start of commercial sales of Epidiolex at American market in November 2018. Some analysts predict that its sales in the USA can exceed $1 bn. The first months of sales showed impressing results, much better than expected.

Provided there are no strict legislative limits from FDA on the way of cannabidiol in the USA, these analysts’ prognoses can turn out too modest. Within just several years cannabidiol from little known health supplement made a great leap to various categories: foods and confectioneries, cosmetics, animal goods and others.
The key to fast CBD sales is wide distribution at the American market. The products rich in CBD can be bought online, at a supermarket, at a cafe or the biggest drugstore chain – virtually everywhere in the USA where it does not have any limitations. Yet at the federal level FDA objects to add CBD in ready-made foods. In case a compromise in this issue is found (market experts expect it to happen) the market will sharply accelerate in the nearest future.

CBD producers that were pioneers at the American market turned from small private projects into big firms that after liberal law adoption, can easily attract credits and strategic investors. For example CBDistillery company from Colorado in 2015 started manufacturing CBD from industrial hemp and selling it through a small commercial site. During the first week it got orders for 70 thousand dollars. In 2016 the company’s turnover amounted to $200 thousand and in last year it reached $4 mln. In 2019 they plan to make $80 mln.
Beyond the USA cannabidiol still has to make a long market way. At the neighboring market of Canada cannabis manufacturers hope to see CBD on supermarket shelves in several years. However, so far because of legislation imperfections, CBD is regulated in the same way as cannabis. After the legalization, it became accessible in licensed stores.
According to Brightfield Group report, in 2018 the European market of CBD amounted $318 mln and is expected to grow up to $416 mln. The prognoses for 2023 is CBD growth by four times to $1.7 bn.
Concentrated CBD extracts (tinctures) are expected to become the main product category that will form a market of $0.5 bn. The markets of creams, capsulated forms and cartridges for vaping by that time will increase to $0.3 bn each. Probable approval of CBD according to EU instructions on new food products will open the way to even wider distribution by adding CBD to foods as a functional component.
THC vc alcohol
Two groups
In 2016, the share of cannabis consumers amounted to 3.9% of the world’s population or 192 mln people by rough estimation by WHO*. By comparison, the share of alcohol consumers ran at 43%, i.e. was 11 times higher.
* People aged 15-64, who consumed cannabis at least once a year.
Over the recent 10 years, the popularity of alcohol in the world has been decreasing, while the cannabis popularity has been increasing with an acceleration trend. Accordingly, alcohol consumers’ share has decreased by 2.1 p.p. while cannabis consumers’ share has grown by 0.2 p.p.
In order to find out why this is happening, we again have to go back to medical issues.
During the previous century, researches of relations between alcohol and cannabis normally revealed a positive connection between them – heavy consumption of alcohol, tobacco and drugs correlated to frequent consumption of cannabis and vice versa. At that, the researches themselves accepted that their results could have been distorted by people selection for the control groups. The respondents were often prone to heavy use of any psycho-stimulants due to low self control. Yet up-to-date researches differentiated by social groups, reveal more complicated relationships and substitution effect too.
So, the most negative situation is a simultaneous consumption of THC and alcohol by heavy consumers, which leads to higher concentration of THC in the blood* and fast intoxication due to cumulative effect.
* Ethanol increases plasma delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) levels and subjective effects after marijuana smoking in human volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2001
According to polls, carried out by Deloitte in the USA, 20% of cannabis lovers always as a rule consume of together with alcohol, 55% rarely combine the two psychostimulants and a fourth of respondents never do it.

A part of the first group consumers belong to heavy alcohol consumers with low self-control level. They are rather impulsive than reasonable in taking decisions and combining may seem the most appropriate variant to achieve a strong feeling of euphoria. Let us note that heavy consumers though drink the main volume of alcohol but account for a small part of all consumers.
At the same time, much more numerous light alcohol consumers can often prefer cannabis to alcohol or completely switch for it if they have such chance*. They would see a more practical way to reach relaxation and pleasure in cannabis due to its rapid effect (when smoking), milder hang-over and viewing cannabis as a less harmful psychostimulant.
* Commentary on «The impact of the legalization of recreational marijuana on college students». Addictive Behaviors. 2019
In this group such motive as comparing the potential harm of alcohol and cannabis is gaining significance. If we take into consideration a lot of factors ranging from immediate effect on the body to social harm, cannabis looks a less harmful alternative in many respects.
Score 11:1
It is obvious that ethanol and cannabinoids are absolutely different substances that differently influence the nervous system. The alcohol has to reach a high concentration in blood and cerebral fluid in order to change the electrophysiology of the brain. THC works in quite a different way due to its high similarity to cannabinoid receptors.
For example, one drink, a small dose of alcohol that can be felt by people, corresponds to equivalent of 12 g of ethanol. At the same time most of people will feel the effect of 0.01 g of THC. Thus, the direct toxic effect from THC consumption is by several hundred times lower than from minimum dose of alcohol.
If we speak of critical effect on organism, the deadly dose of alcohol for people is about 8g per kilo, while it is 3g per kilo in case of THC*. Obviously, critical doses of alcohol are very often taken, while it is difficult to imagine a critically toxic dose of THC even in case of excessive consumption.
* Marijuana poisoning. Top Companion Anim Med. 2013
 Other effects of cannabis consumption can pose danger. In most of countries it is considered to be a narcotic drug, that is a substance leading to addiction and serious perils of abuse, harm to man’s health and society.
Other effects of cannabis consumption can pose danger. In most of countries it is considered to be a narcotic drug, that is a substance leading to addiction and serious perils of abuse, harm to man’s health and society.
In assessment of harm from narcotic drugs, the fifth edition ‘Diagnostic and statistic guidance on psychic disorders’ (DSM) is an up-to-date standard. According to this guidance, there are 12 criteria of assessing all psychoactive substances. American researches have made a very interesting comparative analysis of psychoactive stimulants*.
* Analyses related to the development of DSM-5 criteria for substance use related disorders: 2. Proposed DSM-5 criteria for alcohol, cannabis, cocaine and heroin disorders in 663 substance abuse patients. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012
Cannabis turned out to be 2-3 times less dangerous by the most of DSM criteria. In particular, alcoholics have bigger problems with 1) development of tolerance to consumed volumes; 2) control over the consumed volume, 3) ability to stop, 4) unproductive time waste, 5) ignoring important issues, 6) further consumption despite health problems, 7) problems at home, work or studies, 8) further consumption despite realizing these problems and 9) strong craving for alcohol. According to the tenth criterion, alcohol consumers had problems with the law 18 times more often than cannabis consumers.
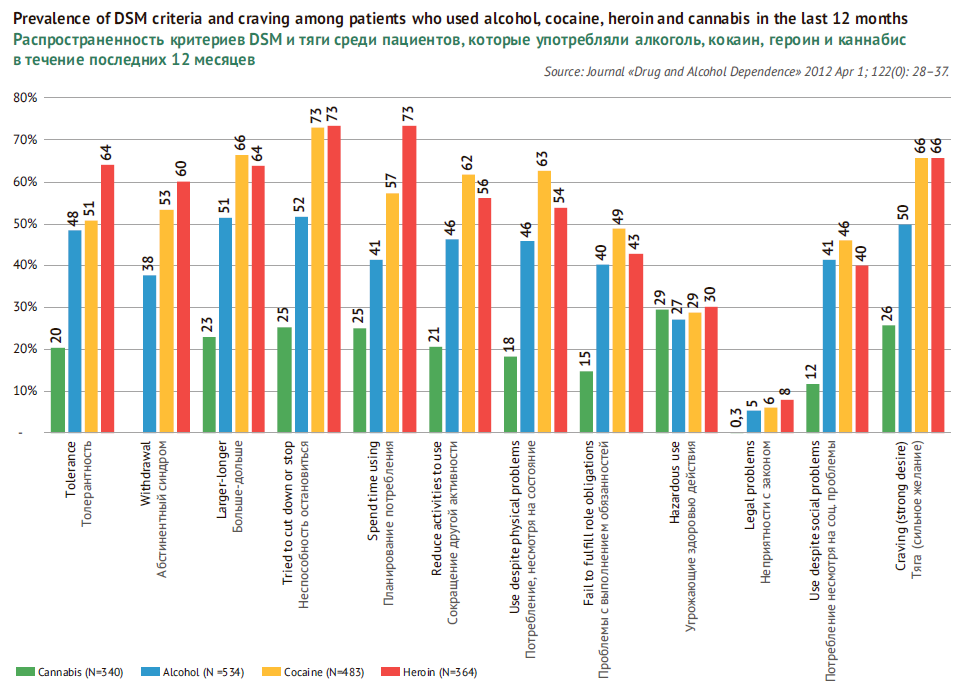
The only 11th criterion where alcohol and cannabis are almost equal is probability of actions that can lead to direct danger to life or health. In this connection there has been published a range of articles on danger of driving and increased number of car accidents in the USA states where cannabis legalization took place. Lower self- control and slower physical reactions is a serious problem for cannabis legalization.
German and Canadian doctors also carried out another risk estimation*. They analyzed a lot of medical researches published in Pubmed. Basing on these data analysis, they drew a conclusion that the risks of cannabis consumption might have been overestimated in the past. And on the contrary, the risks of alcohol consumption are often underestimated.
* Comparative risk assessment of alcohol, tobacco, cannabis and other illicit drugs using the margin of exposure approach. Sci Rep. 2015
All said above does not mean that cannabis (or rather THC) is safe. In state regulation the comparison of psychostimulants is considered incorrect and lesser harm of cannabis is called a false argument to its favor. Even if cannabis is as dangerous as alcohol should it be made publicly accessible?
Yet the proportion of harm and good is very interesting for modern consumers, as many of them are well-disposed to psychostimulants but pay much attention to their health and have a critical look at them. It is easy to find a lot of adaptive researches of cannabis and social media it is more and more opposed to alcohol.
Two-storey market
So in what way do the markets of cannabis and alcohol influence each other provided relative availability? Here the most important part is played by heavy alcohol consumers because of dependence on it.
Before becoming a heavy consumer, light consumer has to make a choice in favor of alcohol and confirm it for some time. As we have already found out from the modern researches, cannabis consumers have twice weaker dependence by DSM scale. But we also found out that in case of cannabis availability, and provided there are efforts to control bad effects, the choice will be most probably done in favor of cannabis.
As a result, we can see two typical models of cannabis and alcohol effect – negative synergetic when the growth of cannabis availability makes the situation worse for a part of heavy alcohol consumers. And the second, positive one, substituting model as cannabis is becoming a healthier alternative for a part of light alcohol consumers.
If we combine these two processes and the current trends, we will see a two-storey market and opposite effects of the growth of cannabis availability in short term and long-term perspective:
1) Currently the most of alcohol is consumed by comparatively small share of heavy consumers. This group contains disproportionally many people from blue collar, mature people as well as people of lower income and to a big extent forms low income consumers’ group. They are naturally limited by cannabis high price and their conservatism.
But for well-provided for and unconservative heavy consumers the immediate accessibility effect means bigger alcohol consumption due to drop in self-control in case of simultaneous consumption. This “subgroup” can cause a loss of substitution effect and a growth of the total volume of alcohol consumption and sales soon after improvement of cannabis availability.
Yet, over the time, the share of heavy alcohol consumers due to natural reasons will decrease provided it is slowly renewed.

2) Numerous researches show that over the recent ten years there has formed a downward trend of heavy alcohol consumers’ number as well as decreasing of frequency and volumes of consumption among teenagers and youth. This is obviously happening due to more responsible approach to health, viewing alcohol as a harmful product and its poor compliance with successful life.
At the same time, new generations are developing a better image of cannabis as a trendy, alternative and nontoxic psychostimulant. In the longer term (due to lower popularity of alcohol and general going off this alcohol course) the share of its active consumers will decrease at higher speed which means a general decline of alcohol sales volumes. And as consumers of higher social levels improve their well-being, they will be responsible for rapid growth of cannabis consumption in the medium term.
Aged people who for medical reasons have to stop consuming alcohol can also switch for cannabis. Besides, in some regions there is no sharp dualism of generations’ attitude to cannabis (ex. India and the USA).
Cannabis and beer
Comparing consumers’ profiles, we can see that so far they overlap not much.
- Beer is viewed as a more masculine and manlier product for mature people engaged in physical labor. It is often considered a drink of the blue color. Cannabis attracts more female audience, students and people of artistic professions.
- Beer is often drunk at big parties and communication is an important motive for consuming beer. Cannabis is a communicator too, but it is a more individual product taken to improve personal condition.
- Beer quenches thirst and has a pleasant taste. Cannabis smoke is pleasant not to everyone and processed cannabinoids are much often preferred in confectionaries than in drinks (so far).
The group of craft beer lovers with their tastes and interests coincides with cannabis lovers more as these two products have a lot of properties that are very interesting to discuss in a club of dedicated and sophisticated consumers. They are often joined by the product authors’ enthusiasm who value the idea not less than commercial success.
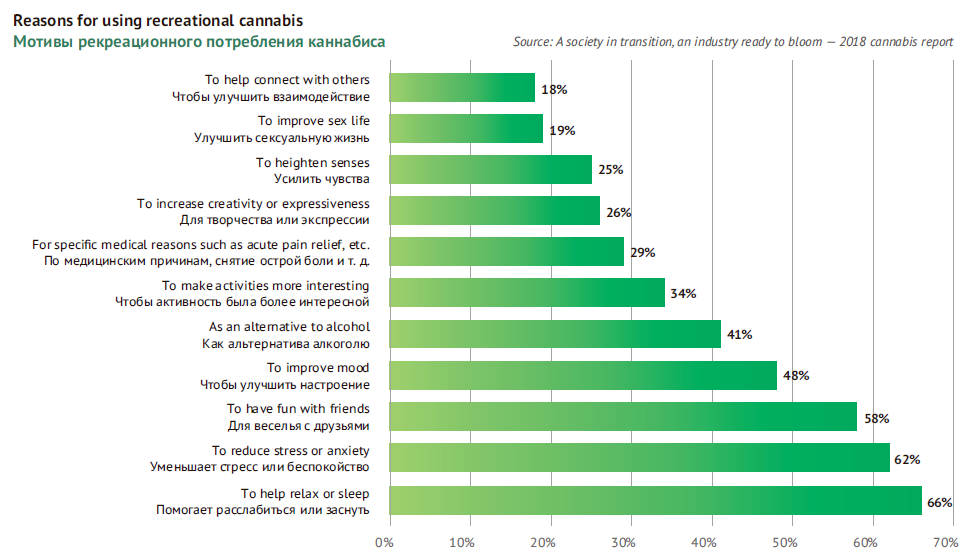
Through the example of the American market, we cannot so far say that the legalization parade influenced the alcohol market in general. Under the industry associations’ estimations beer volume sale decrease, yet the market of strong alcohol has even grown a little recently.
However as we have already stated, the legal status of cannabis does not have the decisive significance for the market development. What is more important is tolerant attitude and absence of actual legal consequences for consumers. We have also found out that heavy consumers that drink strong alcohol can even stimulate sales in the short run.
The long-run national trend of decreasing beer sales is more representative here. Due to comparatively high price of cannabis the major competition with beer takes place at the premium market. The premium segment of the American beer market is craft and import that take a share of mass brands. The sales growth of craft beer has slowed down abruptly in 2014-2017 having coincided with the legalization wave.
Even for a person with imagination it is difficult to foresee the future of drinks with THC and CBD and the way they will interact with alcoholic drinks. For example, imagine the situation of cannabis consumption in a family even in a most tolerant society.
In the future alcohol manufactures themselves, for instance major brewing companies, can make a contribution into switching their consumers to drinks with cannabinoids. This emerges from higher investment interest and recent trends in the USA market.
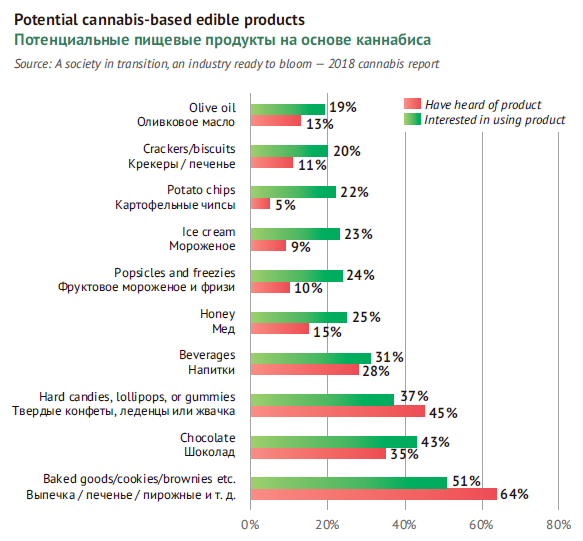
It is not likely that THC and C2H5OH would meet in a bottle of beer (federal law forbids mixing them), however, there is a good chance TCH can substitute alcohol in this beer.
Cannabis and related combinations can give beer new flavors and tastes hop does not have. Cannabis producers are actively selecting which resembles the history of hop-growing development due to which the content of alpha-acids stopped being the only property of hop. Terpene profile of cannabis (essential oil composition) is equally complex as hop profile for craft brewing.
Not only THC but also CBD will be widely used as a functional component of food industry, as the healthy life style is gaining popularity and as people growing aware of it. As long as CBD is not a standardized product, its application is limited. Yet in the future, from the marketing point of view, drinks with CBD will be positioned as “meditating”, relaxing recommended after physical and emotional overloads as well as for stress releasing.
CBD can be opposed to alcohol and energetics or be in content of such drinks as a compensating element. Obviously in drinks that contain THC, CBD from the original cannabis material will be also present or added.

Combining categories of cannabis and beer is connected to solving a technological problem. As cannabinoids dissolve in fats, it is necessary to use special surface-active agents to bind fat and emulgents to make them dissolve in water. As a result, bioavailability improves considerably and the speed of cannabinoid effect on the body grows.
Currently two complex technologies to bind cannabinoids at molecular level based on biochemical and mechanical principles are applied.
1) Liposome use. These are many-layers fatty spherical structures that can capture cannabinoids and easily enter blood through GIT.
2) Nano-emulsion application. This method is based on breaking cannabinoids via ultrasound into nano-scale particles, that can form stable solutions in water with emulgent. This method has a benefit in decreasing the volume of emulgent that raises the price for a drink and affects its taste.

Obviously Californian craft brewery Two Roots Brewing Co (a part of Cannabiniers, a major player of cannabis market) took the second way. In mid 2018, at the capacities in Nevada, the brewery manufactured an alcohol-free craft cannabier thus creating a new market category of drinks for adults. Let us note that some of other companies working in Nevada already have a wide range of products combining THC and CBD in fizzy, energetic, fruit drinks and even in milk cocktails.
The formula used in the beer range of Two Roots was developed for imitation of alcohol effect, which starts in 5-10 minutes and finishes in 1.5 hours. In general, this is the clear answer to the issue of cannabinoid transport in the body.

In the brand range one can find various beer styles, popular among craft lovers and various balance of THC/CBD. According to company director’s message the average price for a can of beer amounted to just 5 dollars, so craft lover are not likely to see any significant difference in price.
According to the original strategic plan, the company started at equipment to the capacity of 50 000 barrels of beer per year (0.58 mln dal). And by the end of 2019, it is supposed to operate at capacities for 500 000 barrels (5.8 mln dal) through contract filling or acquisitions. After the production and sales started in Nevada, Two Roots Brewing had to adjust their sales plans as the actual demand was three times higher than prognosed and new clients had to wait their orders for three months.
The Californian expansion into San-Diego, Los-Angeles, San-Francisco was connected among other things to the fact that the cannabis market in that state was estimated at 2.5 bn in 2018. But a lot of companies and organizations linked to the industry of cannabis got interested in the production, and supported sales development at the sub-national level.
Potentially, the cannabier distribution will be preset in 20 sates of the USA. Two Roots Brewing plans to achieve the sales volume of 500 000 barrels by the end of 2020, or even earlier. In order to profit from the pioneer’s advantage, the company is making agreements with strategic investors and craft brewers. The company’s plans can be ruined by the expected launch of alcohol-free beer with cannabis by brewing giants.
To get the full article “Cannabis: product that changes markets” in pdf (52 pages, 16 diagrams) propose you to buy it ($30) or visit the subscription page.
2Checkout.com Inc. (Ohio, USA) is a payment facilitator for goods and services provided by Pivnoe Delo.
The article materials have been prepared using data by WHO and INCB. A number of estimations are based on presentations of cannabis producers and reports by analytical companies: Brightfield Group, Ackrell Capital, Gallup, Arcview, Prohibition Partners, Cowen Research and New Frontier, Deloitte. Publications in Yahoo Finance, Forbes and Bloomberg were used in the article preparation. The data on scientific researches and medical information concerning cannabis consumption were taken from database of medical and biological publications Pubmed.
In case the information source is not provided, the data and their interpretation are our assessment based on the current trends.
We do not guarantee that the given information is absolutely correct, though it is based on data obtained from reliable sources. The article content should not be fully relied on to the prejudice of your own analysis.

